Your key to success: Sales lead qualification

Some of the top priorities for your B2B company is demand generation, and sales lead qualification. The challenge is finding and qualifying good leads that inside or outside sales or distributors can convert into buyers.
Learn how to increase your chances of closing more deals by filtering and qualifying leads for yourself and your team. Maximize your sales pipeline with proven sales lead qualification, lead nurturing and lead management processes that work for many businesses. Scroll on for more details.
What is sales lead qualification?
Sales lead qualification is the process of evaluating and determining the potential of a person or company to buy your product or service.
Prospecting is the first step in your sales process. It’s about finding customers interested in your product or service and getting them to understand what you offer.
The first step in prospecting is qualifying leads. It means you need to find out if there’s a good chance that they’ll buy from you or not.
Qualifying prospects is crucial because it helps you understand your target audience and identify companies that need your product. Also, it enables you to reduce your time on opportunities that you’re unlikely to convert into customers.
How does a sales lead qualification process benefit you?

How to generate B2B sales leads?
Typically, you can use two lead generation methods: inbound and outbound marketing. Inbound methodology activities include social media, content marketing, eCommerce, websites, and videos. Also, you can develop leads through outbound activities, such as telemarketing, direct contact, trade shows, email marketing, advertising, etc.
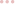
Types of sales leads
A sales lead qualification process generates the following leads:
Unqualified leads (UQL): These are leads your marketing team is working on to qualify and hand over to SDRs.
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLS): They’re qualified prospects you can interact with through email campaigns, social media channels, etc. MQLs have a high chance of being buyers.
Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs): These are MQLs who’ve shown interest in your product or service and are ripe for a chat with your sales reps.
Product Qualified Leads (PQLs): These leads are highly likely to purchase your product because they’ve either started a free trial or a freemium subscription.
Conversion Qualified Leads (CQLs): A CQL is a lead who has converted by registering for a webinar, completing a form or downloading a resource, etc.
Characteristics of a qualified prospect
How can you know if you’ve got a qualified prospect? Here are the features of a qualified prospect.

Qualifying questions
Qualifying questions are the questions that sales professionals ask to determine if a prospect is worth pursuing. Asking questions assesses the potential of an opportunity and is an integral part of the sales process.
Some qualifying questions are:

It’s also necessary to disqualify prospects during the sales lead qualified process.
When to disqualify a prospect?
- Limited funds: You can disqualify prospects when they’re not interested in the product or service or don’t have the financial resources to buy. Disqualify a prospect if their current budget can’t allow them to buy from you. But continue nurturing them by sending handy resources addressing their needs.
- The potential customer lacks authority: Discontinue pursuing a lead who isn’t a decision-maker or has no power in determining the buying process.
- The lead is preoccupied with other things: Put the lead in your archive if they show that they can’t have a meaningful conversation with you due to time constraints. They’re not presently ready to chat with you, but you can restart the dialogue later when they can spare some time.
Related: “Sales Prospecting: Definition, Techniques, Process & Tools.”
What you must do first before the sales lead qualification process
Use lead scoring to qualify leads
Lead scoring is a way to measure the potential of a lead and is an integral part of your lead management process. In this way, your marketing and sales teams can identify prospects and prioritize them accordingly.
Also, lead scoring helps you identify which leads are worth following up with and which ones aren’t worth your time.
You can perform lead scoring in many ways, but assigning points to different actions is the most common. When someone fills out a form on your website, they get two points. If they fill out an email form, they get an additional point. Check out the following example.

You can use the following lead scoring models.
1) Marketing-driven: These models are marketing data-driven, such as website visits, clicks, and conversions.
2) Sales-driven: Sales data such as calls, demos, or presentations influence this approach.
3) Hybrid: These models combine marketing and sales data to generate a score for the leads, which helps in prioritizing them accordingly.
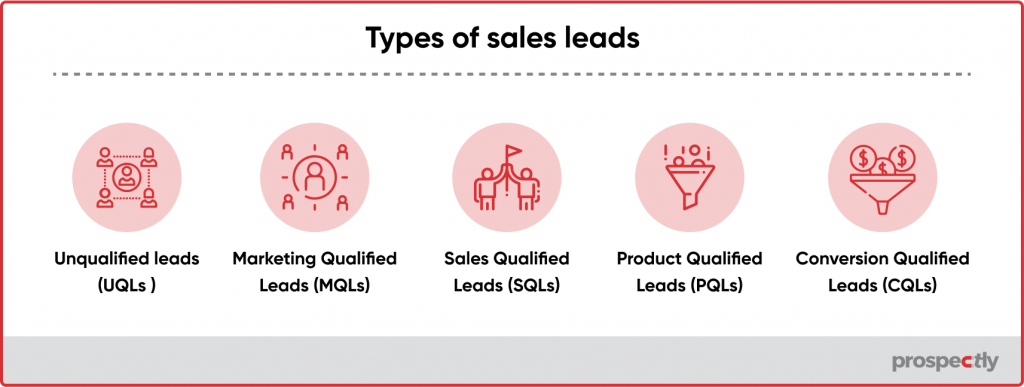
After assigning scores to your leads, you’ll know where the prospects are in the buying process and what your reps should do. See the example below.
Use lead scoring software to score leads automatically.
The next step after lead scoring is qualifying leads by using lead qualification frameworks.
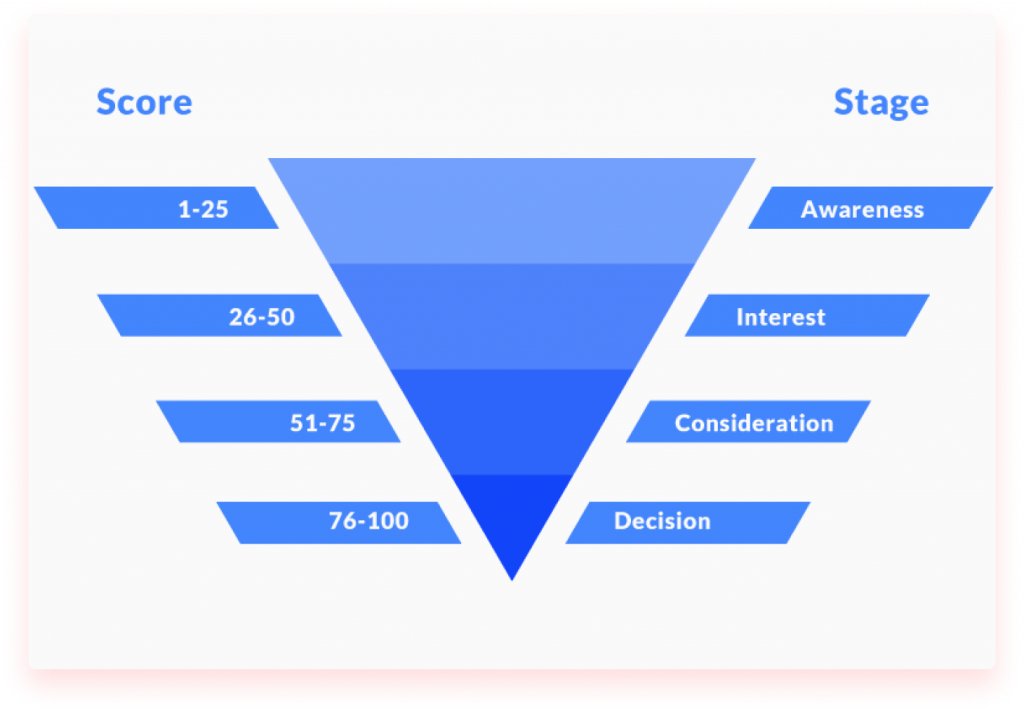
Sales lead qualification frameworks
A lead qualification framework is a guideline that helps SDRs qualify prospects systemically and using data. Here are some popular techniques you can put to the test.
Start with BANT
BANT is still a go-to method for sales lead qualification for many companies and stands for Budget, Authority, Needs, and Timeline. And this is how you can use the framework.
Budget: Does your prospect have the ability to purchase your product/service? For example, you could say, “How does your company allocate funds for this type of solution?” “How much of the budget can your business set aside for the product/service?”
Authority: Is the lead in a decision-making role influencing the product purchase? You may say, “Who else makes the primary decisions regarding buying in your company?” or “Are there any challenges you foresee concerning this transaction, and how can we resolve them right away?”
Needs: What are the current potential customer’s needs-aka the pain points? Here are some qualifying questions you might ask: “Can you tell me about the challenges you’re facing right now?” “What causes that pain, and how do you think this product will improve your condition?”
Timeline: Is the buyer ready to buy? When do you want to solve the problem? “Are there any priorities in your buying process?” “What other solutions are you considering?”
When to use: BANT is ideal if your business deals with high-premium products. So you want to dig deeper to uncover the lead’s ability to pay. Firms with low-priced products can benefit from this model. B2B sales requiring high levels of authority to decide on purchases can also use BANT.
Strengths: Simple to implement.
Weakness: BANT’s questions are illogical- they can make the prospect feel uncomfortable because you start with money. And needs come later. It could appear as if you’re more concerned with selling than understanding what the lead wants first.
Again, many people are involved in complex B2B sales as decision-makers. As a result, you should bring this up in your discovery call questions.
Look to CHAMP
BANT is seller-centric, but CHAMP is more focused on the potential customer. Use this sales lead qualification approach to identify if the lead has challenges that your product seeks to solve. You can disqualify the prospect if there’s no alignment between their challenges and your solution.
CHAMP represents Challenges, Authority, Money, and Prioritization.
Challenges: What challenges does your business want to fix? What problems do you experience that your current solution can’t effectively resolve?
Authority: Who else are the key decision-makers in the buying process? Do we need to bring them into the discussions? Tell me more about the corporate relations that affect the purchase decision.
Money: What’s your budget like regarding this solution?
Prioritization: What are your timelines concerning implementing the solution? Are there any alternatives you’re looking to try?
When to use it: It works perfectly with likely buyers who’ve no idea about what you’re selling. You can quickly determine if they match what your product wants to address.
Strengths: CHAMP’s discovery call questions follow the natural flow that puts the prospects at ease.
Weaknesses: The method lacks in-depth questions because it doesn’t help the seller explain success after using the product. It limits the rep from demonstrating the solution’s value during the proposal period.
Try MEDDIC
This sales lead qualification framework stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion. Here’s how you can use MEDDIC.
Metrics: What does the prospect hope to improve by using your solution in quantitative terms? Do they want to reduce the churn rate or boost the conversion rate? You need to know how the buyer defines their success.
Economic Buyer: Who makes the purchasing decision in your company?
Decision Criteria: How do you evaluate if a vendor meets your requirements? What criteria do you use to make buying decisions?
Decision Process: Describe the processes your business follows to assess a potential purchase.
Identify Pain: What challenges do you want to solve?
Champion: Who else is interested in your product/service in the organization?
When to use it: The MEDDIC lead qualification framework is ideal for brands with low volume and high-value sales, such as software vendors. It gives salespeople plenty of time to gather information about the prospect.
Strength: The potential buyer can see the metrics they can improve with your product.
Weakness: MEDDIC may be unsuitable f0r companies with low-cost products at huge volumes, like eCommerce retailers. The qualification process is longer.
Consider ANUM
ANUM operates on the same principles as BANT but reverses some steps. It stands for Authority, Need, Urgency, and Money. Find out whether the prospect is the primary decision-maker. Understand their needs and urgency to fix the problem. The last step is to assess their ability to purchase the solution.
When to use it: ANUM is an excellent approach when dealing with businesses without clearly defined levels of authority, such as start-ups. That’s because it may be unclear who’s in charge of signing off contracts at the early stages.
Strength: Money isn’t the main qualification criterion for this solution.
Weakness: The rep must demonstrate the reasons for the client to purchase the goods/service.
What about FAINT
FAINT (Funds, Authority, Interest, and Timing) is an alternative to BANT. Like BANT, this model places the company’s budget at the forefront. However, it adds another element in the sales lead qualification steps- interest.
Sellers should find out if the potential customer is interested in their solution. They need to generate that excitement by showing leads how the product can improve their current situation.
When to use it: FAINT is perfect for potential buyers who’ve never seen or tried your good/service. Such prospects include those you want to engage with via cold calling. However, BANT is ideal for people who know what you offer.
Strength: The salesperson can gauge the prospect’s interest in the product.
Weakness: Like BANT, the model scratches the surface in understanding the customer’s challenges.
Opt for HubSpot’s GPCTBA/C&I
HubSpot developed this sales lead qualification framework to emphasize the following aspects.
Goals: How would you rank your priorities at the moment?
Plans: What steps will you take to achieve that goal?
Challenges: Are there any obstacles you foresee with your plan?
Timeline: What is your timeframe for solving this issue? Are there any steps you plan to take if you do not buy at this time?
Budget: To date, how much have you spent on this goal? Can you allocate any additional funds to it?
Authority: What is the process of purchasing products of this type at your company? How are others feeling about this buying decision, and what concerns them? How do I manage and respect ego issues or ownership issues that may arise?
Negative consequences: Why is it essential to reach this goal? How much will it cost you and your business if things stay as they are?
Positive Implications: How will you move forward if you achieve this goal?
When to use it: It’s a model that suits the SaaS industry.
Strengths: Sellers can quickly establish if the potential customer is an excellent fit for their product/service. It provides salespeople with enough details to determine if the lead is worth following.
Weakness: It requires the rep to walk the prospect through all the questions to get as much info as possible. As a result, inexperienced sellers or those unfamiliar with the lengthy technique may sound like detectives to likely buyers.
When to move qualified leads to the next step?
Here are some primary indicators of moving a prospect forward.

Sales process red flags
After doing everything by the book, the customer may remain without an appetite for your solution. Check out the following red flags that show you need to move on and focus on other lucrative opportunities.
- It’s hard to know when a prospect is enthusiastic about your products since they won’t communicate. It’ll prevent you from contacting them repeatedly. Don’t waste your time pursuing the protential customer if you cannot reach them.
- If they can’t or won’t commit, your reps will be less efficient and productive. Your salespeople must make their pitches to someone with authority to approve the sale. Otherwise, you’ll lose the prospect.
- Occasionally, your solution won’t meet your prospects’ needs. That’s fine, and it’s okay to move on if it’s not possible.
Parting words
The role of a sales lead qualification framework is to filter leads systemically. It’s a process that helps you determine the probability of converting a lead into a sale. The model aims to identify the right prospects and weed out those not worth pursuing. Because of this, you can save time and effort in the long run.
Use a sales lead qualification framework that meets your company’s needs and prospects. Tailor it to suit your requirements and make it scalable to grow with you as your business expands.
Related: “16 Sales team management strategies: This is what experts do.”